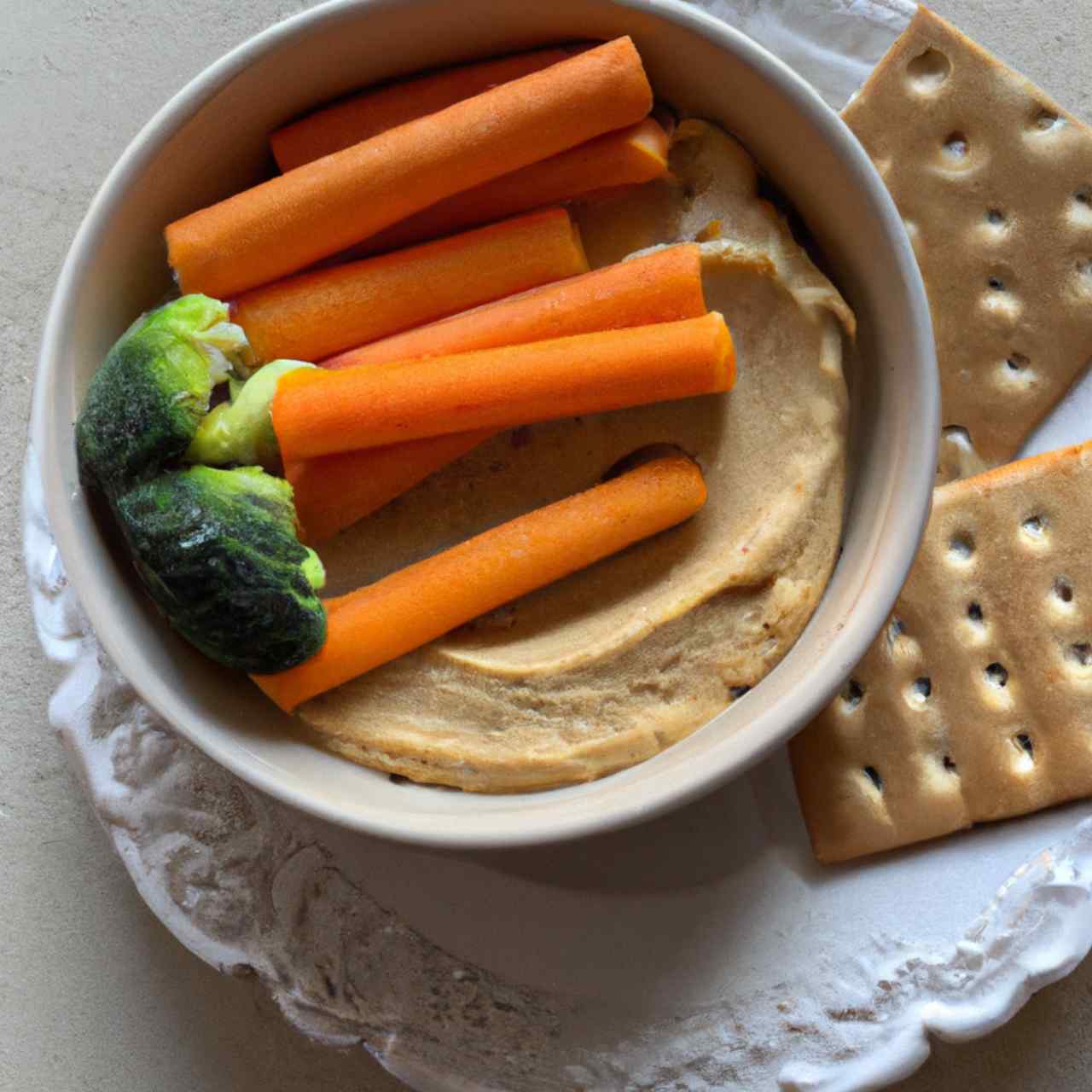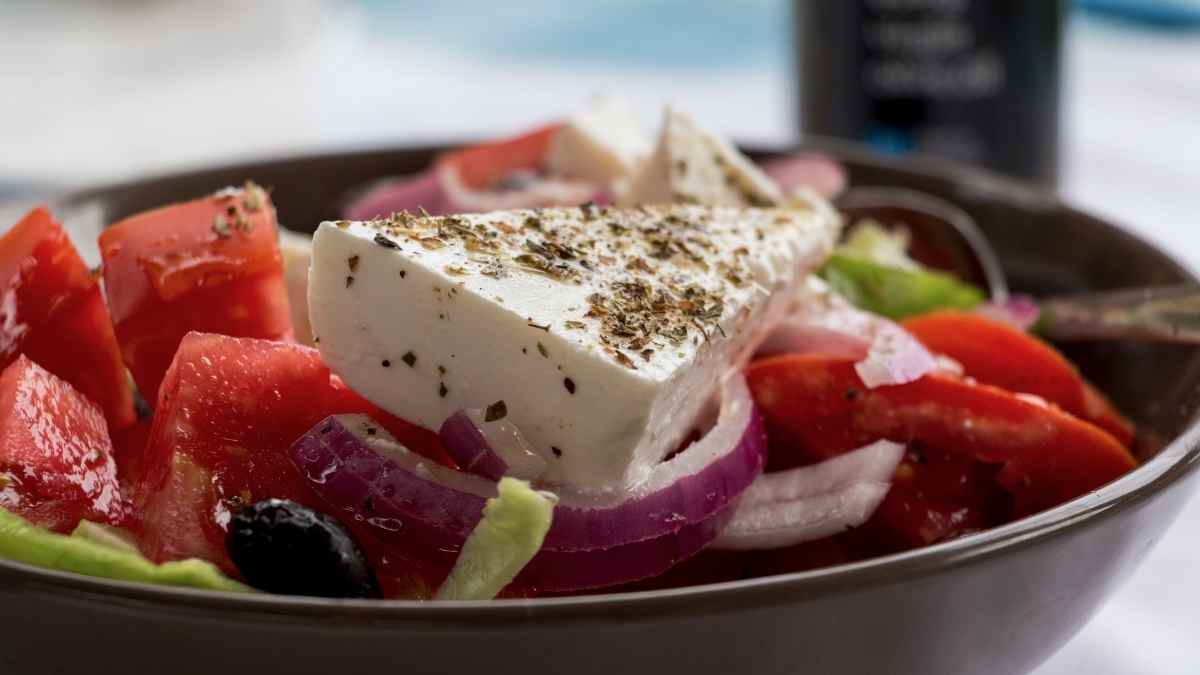Tastes Of Food – Understanding Tastes and Food Flavors
Taste is a complex sensory experience that involves the interaction of taste buds on your tongue with chemical compounds in food. The combination of these two factors determines how you perceive flavors and the ultimate taste of the food.
Taste receptors on our tongue detect and inform us if a food is sour, sweet, salty, bitter, or umami. However, the overall sensation is added to by aromas sensed by your nose.
Knowing how each flavor balances and works with others can help you create amazing dishes and be more confident with cooking.
Cooking is a lot like playing an instrument, but instead of using your hands to play the music, you use ingredients that are cooked in order to create it. In the same way that if you want to make beautiful music, you need to have all the right instruments at hand; so too do you need to know what kind of flavor goes well together before you start mixing them up.
Food Taste Meaning?
If you want to learn more about food taste meanings, then keep reading. The food taste meanings are a series of symbols used to describe the flavors of foods. These symbols are based on the five basic tastes: sweet, sour, salty, bitter, and umami.
These symbols are often used in cooking classes and culinary schools. They are also used in restaurants and bars to describe dishes.
Here are the food taste meanings:
What are the 5 basic tastes?
The 5 basic tastes are sour, sweet, salty, bitter, and umami. These five basic tastes can also be combined into more complex flavors such as bitter-sweet, savory-umami, etc., but they all have their own unique characteristics. Sweetness is the most common flavor we experience on a daily basis.
What is the Taste of Sweet
The sweet taste is one of the most common tastes we experience in our daily eating. It is a pleasant experience which is why sweet is a very popular taste. We all have someone in our friends or family who is a “sweet tooth.” How do we describe sweetness? Well, it is definitely a pleasant taste, usually indicating the presence of sugar.
See Our Recipe for Black Forrest Cake as an example of sweet food, or a waffle bar that contains salty, sweet, and sour.
What is the Taste of Salty
Saltiness can be defined as a sensation caused by the perception of salt on the palate. Saltiness is one of the five primary tastes. The most common sources of sodium are table salts, processed foods, canned goods, pickles, cheese sauces, soups, bread products, etc.
The addition of salt enhances flavor and makes food more palatable, as long as it is not overused or too much is added.
What is the Taste of Bitter
This one may seem counterintuitive at first because bitter flavors are usually associated with unpleasant sensations. But there is actually an important role for bitterness in food. Bitter compounds stimulate salivation, helping with digestion. Some people love bitter, a good example would be beer which has a slightly bitter taste from the hops.
What is the Taste of Sour
Sour – This one may seem obvious but sour is actually quite complex. Sour flavors are derived from acids found naturally in fruits and vegetables. The acidity levels vary depending on what type of fruit or vegetable they come from. For example, lemons contain citric acid while limes contain tartaric acid. Acids also play an important role in cooking by breaking down proteins into smaller pieces for easier digestion. Vinegar is another example of a sour or tart-tasting food that is used to bring out the good flavor in food – e.g salad dressing.
What is the Taste of Umami
Umami
This one is tricky because umami is an umbrella term describing savory tastes including glutamate, glutamine, nucleotides, peptide hormones, amino acids, etc. Umami is commonly associated with meat products but can also come from vegetables and dairy. This taste is best experienced by chewing slowly and thoroughly before swallowing.
It is important to note that umami does not necessarily mean rich or fatty; instead, it means complex and full-flavored.
What to Know About Your Sense of Taste
Your sense of taste is located in your mouth on the back part of your tongue. It consists of two parts – a front section called the tip or papilla that detects sweetness, saltiness, acidity, bitterness, and umami flavors; and a rear area called the foliate papillae that detect sourness, astringency, and fat content. The receptors for each type of flavor are found at different locations along these sections of the tongue.
Taste It’s a Matter of Balance
Now for the balancing act. You need to find ways to make sure your dish doesn’t become too heavy on one side or the other. If you’re making something rich like chocolate cake, don’t add sugar because it will overpower everything else. Instead, use honey or maple syrup to bring out the sweetness without overwhelming the rest of the ingredients. Similarly, adding vinegar or lemon juice to salad dressing helps cut through richness while bringing out freshness.
What does Hummus taste like?
\What does Hummus taste like? – What is the texture and flavor – see our full answers!
What Does Jajangmyeon Taste Like
Jajangmyeon is a delicious and hearty dish that is perfect for a winter meal.
What Does Chamomile Tea Taste Like
What Does Chamomile Tea Taste Like – and How to Make It Taste Better
What Does Taro Taste Like
What Does Taro Taste Like – Similar to sweet potato of some style of yams.
What Does Pesto Taste Like
What Does Pesto Taste Like- How to get rid of the peppery taste in pesto?
Star Fruit Taste – How To Eat a Star Fruit (and Love it)
What Does Start Fruit Taste Like – How Ripe Does It Need To Be?
What does jackfruit taste like
What does jackfruit taste like – some say pork others beef – but actually it just a great meat alternatve.
What Does Duck Taste Like?
What Does Duck Taste Like? – We explored Farmed Duck, Wild duck and Duck Eggs
What Does Quorn Mince Taste Like
What Does Quorn Mince Taste Like – And how to make a great meat alternative.
What Does Feta Cheese Taste Like
What Does Feta Cheese Taste Like – not very salty if you rinse off the brine.
What does Kool Aid taste like without Sugar
What does Kool Aid taste like without Sugar and some sugar alternatives
What Does Cornstarch Taste Like
What Does Cornstarch Taste Like – no if used properly it should be nuetral
What Does Fondant Taste Like
What Does Fondant Taste Like, what is the flavor and texture – we tell it all.
What does Matcha Taste Like
What does Matcha Taste Like – we teach you all about match drinks and their tastes.
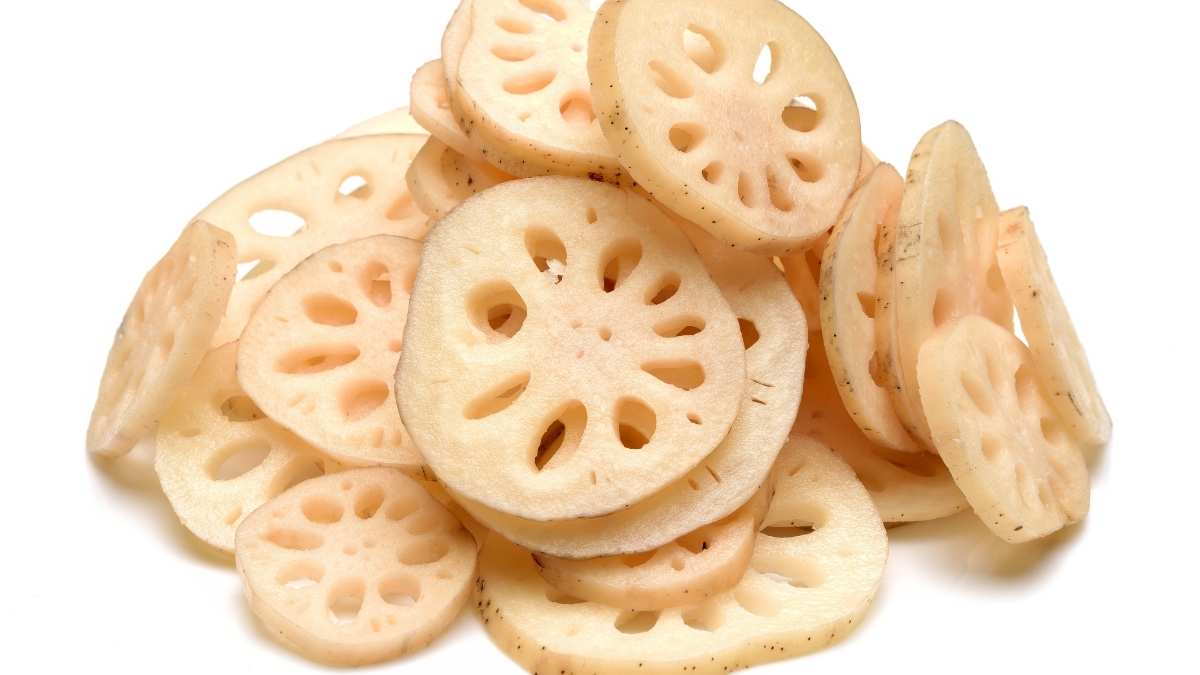
What Does Lotus Root Taste Like
What Does Lotus Root Taste Like – Raw, cooked we give you a great taste and texture profile.
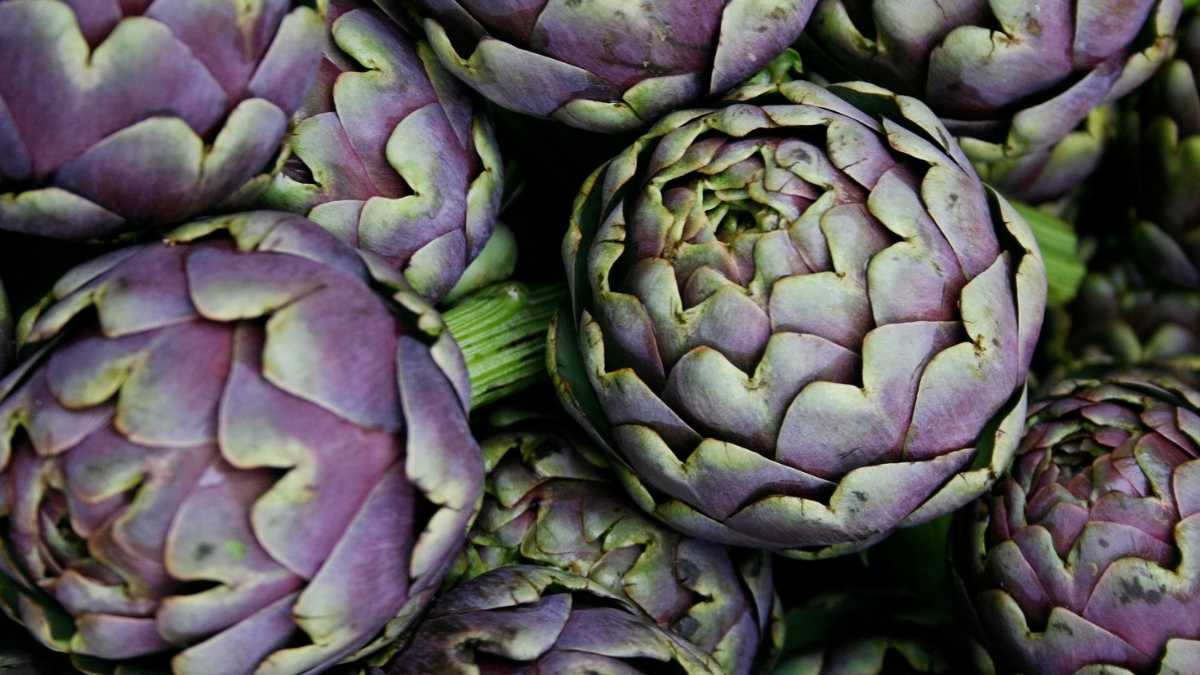
What Does Artichoke Taste Like
What Does Artichoke Taste Like – We taste the Top 5 ways to cook them.